India Protectors Alliance – Catalytic achievements with the support of HUL, BMGF and RBL Bank
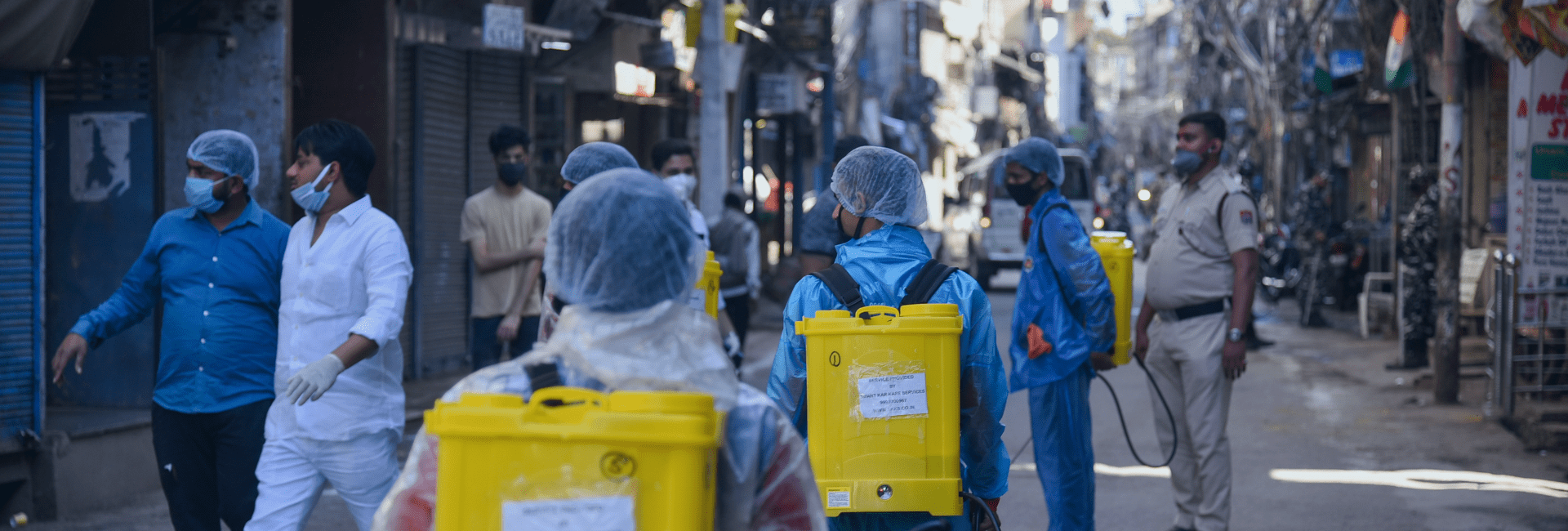
Over the past two years, we have experienced a unique and unprecedented situation due to the COVID -19 outbreak and subsequent lockdowns. The multiplicity nature of COVID-19 needed an all-hands-on approach that saw corporates, philanthropists, civil societies, and individuals come together to support immediate relief efforts and save lives.
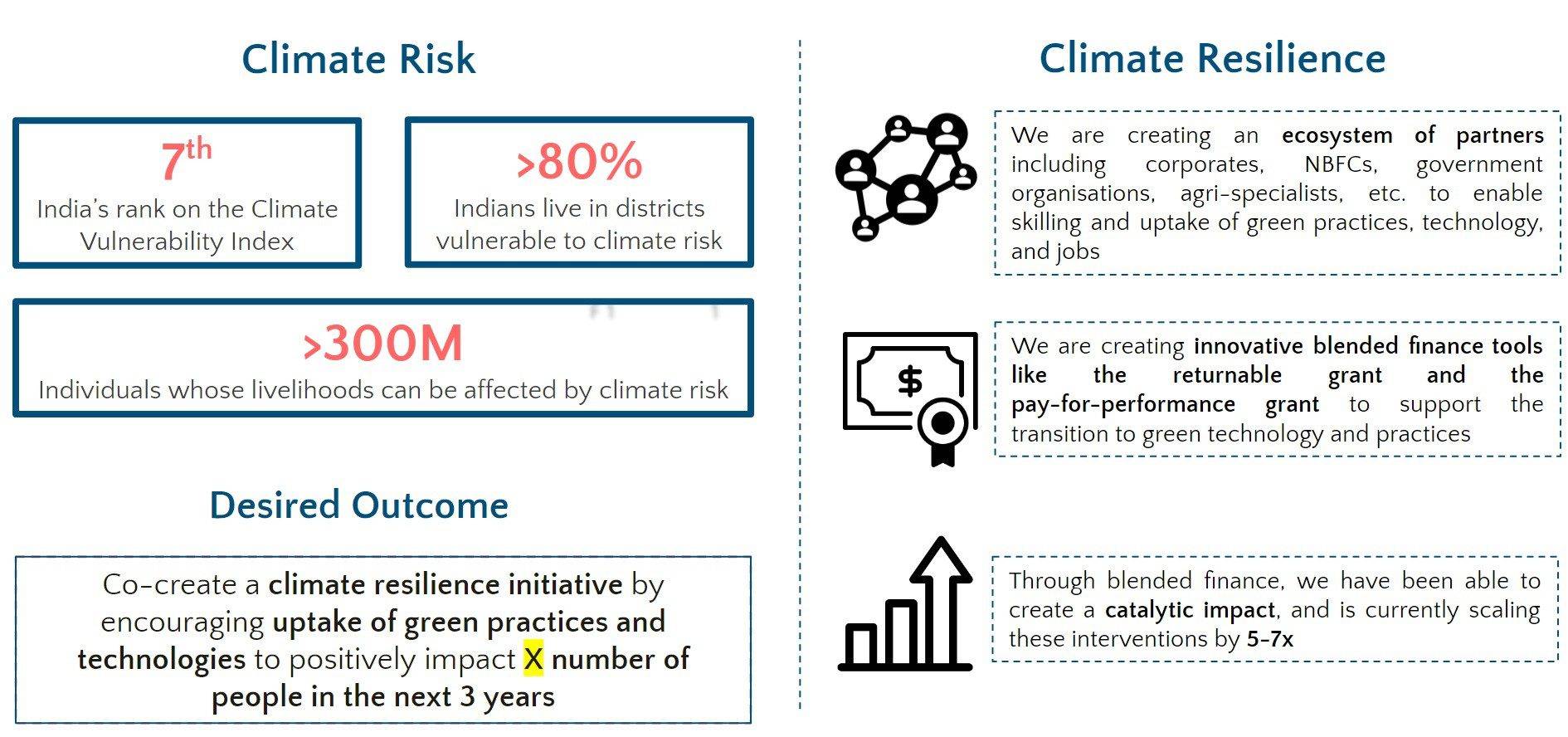
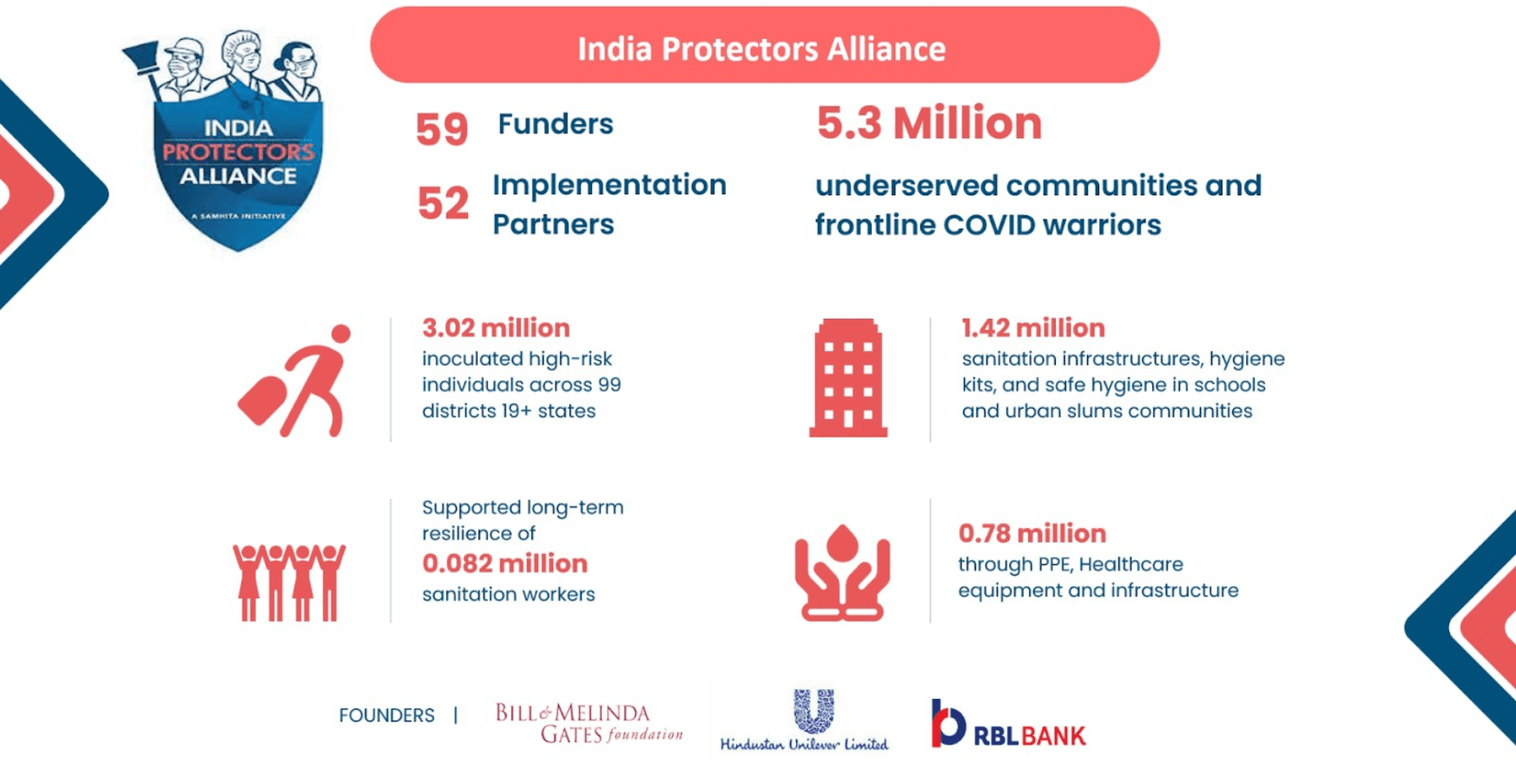
Corporate India and non-profit organisations’ response to the COVID-19 pandemic has shown the sector at its best to create a better normal, such as The India Protectors’ Alliance (IPA). The IPA was founded in early 2020 with the support of Hindustan Unilever, RBL Bank and Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation to protect the most vulnerable and at-risk communities. Through this INR 92 Crores Alliance and the collaboration of 59 funders and 52 implementation partners, we have impacted over 5.3 million beneficiaries across underserved communities, vulnerable populations, and frontline Covid warriors such as healthcare and sanitation workers.
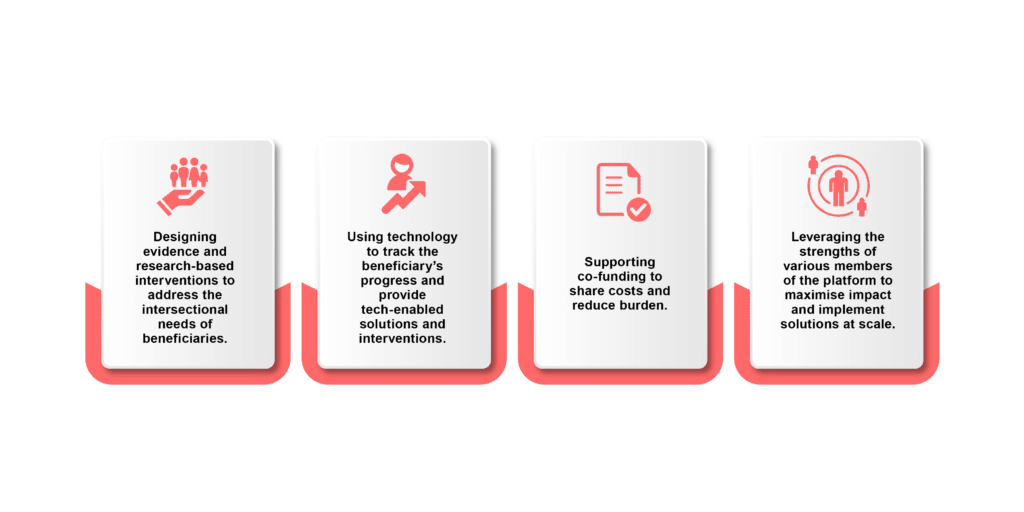
IPA’s Approach: what we did & how we did it
IPA was constituted to equip workers in the healthcare and sanitation sectors to pursue their livelihoods safely by protecting them from COVID-19.
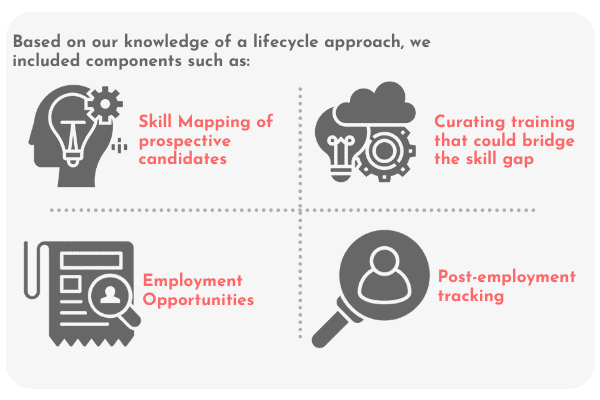
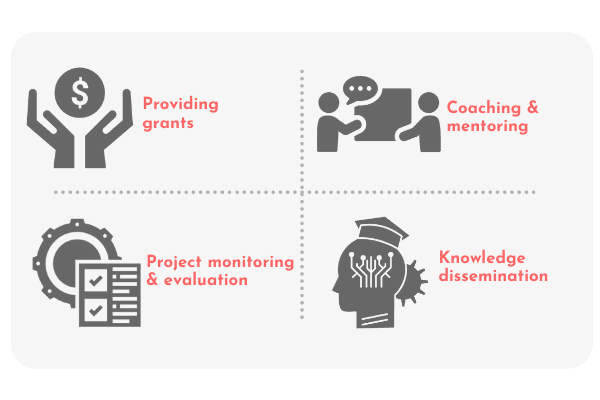
Initially, IPA helped fulfil immediate and critical needs like PPE kits and masks for the frontline health and sanitation workers. However, as the body of knowledge about COVID-19 and its management evolved, IPA too evolved to incorporate other interventions, especially during the second wave of the pandemic. We began working on training and capacity building programmes, providing
Key principles followed:
Our Achievements
Total Beneficiaries : 5.3 Million
A) Healthcare Interventions
Strengthening the COVID-19 vaccination drive: We have inoculated over 3.02 million citizens in high-risk and remote areas across 99 districts in 19+ states through our COVID-19 vaccination drives.
Enabling access to critical care equipment & protective gear: Protective gears were supplied to frontline healthcare workers and police officers. Key medical equipment such as ECG machines and maternal monitors were also supplied for regular patients. 30 implementation partners helped supply this equipment across the country, thus helping us reach over 0.35 million people.
Addressing the medical oxygen crisis: In partnership with nine implementation partners, IPA procured and distributed 950 oxygen concentrators and set up four 500 LPM oxygen plants across the country. This helped impact over 0.3 million hospital patients across the country.
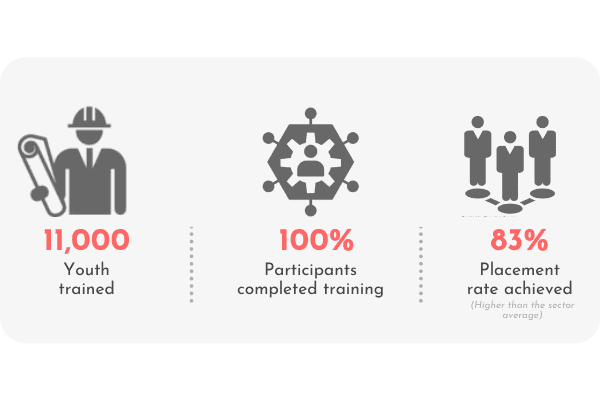
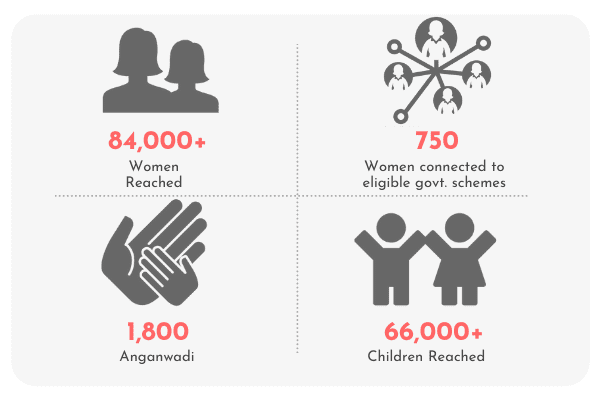
Training on COVID and non-COVID skills & knowledge: Through capacity building of healthcare workers and community awareness programs, we impacted nearly 0.13 million lives.

B) Sanitation Interventions
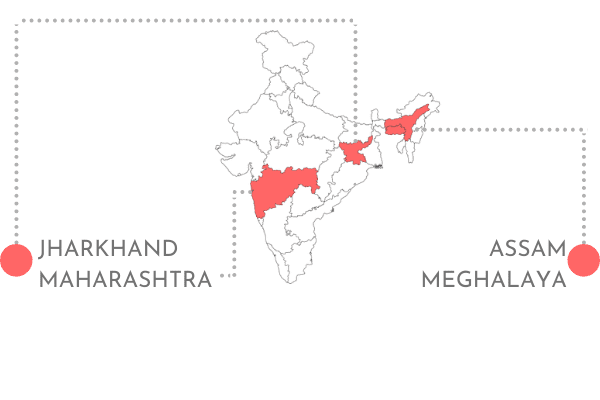
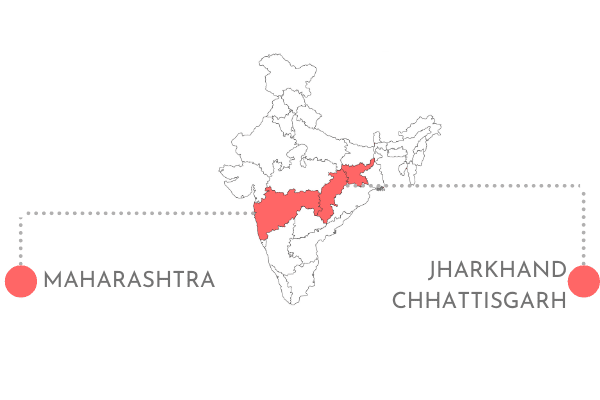
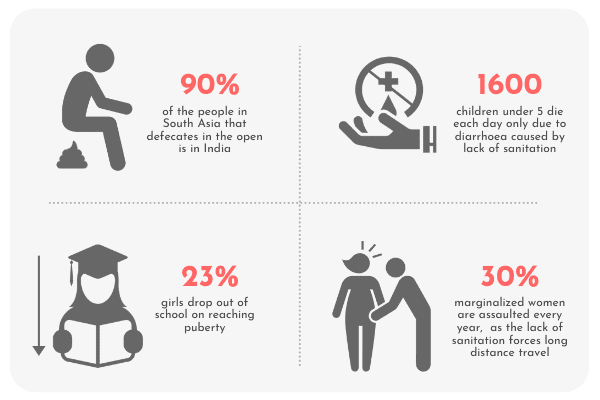
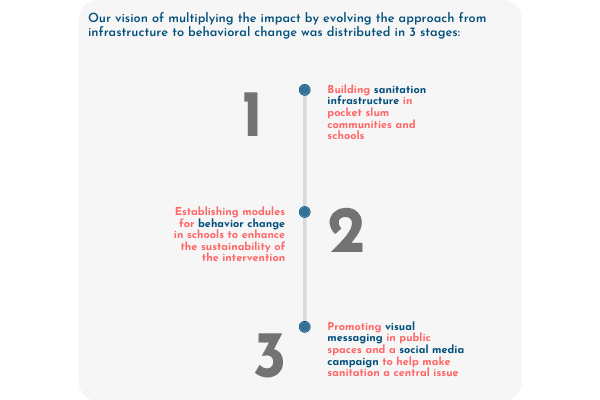
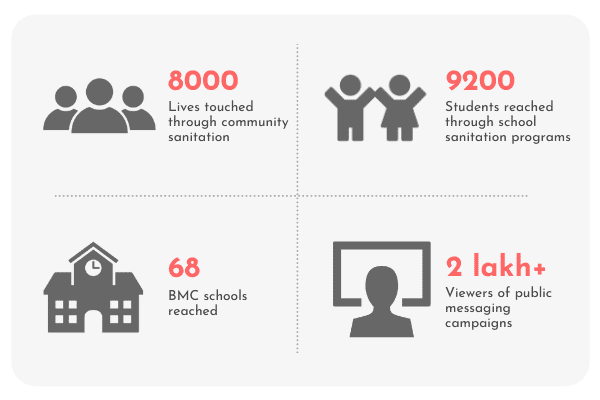
Strengthening community sanitation : Safe sanitation interventions were initiated across Maharashtra to build and improve access to sanitation infrastructures in schools and urban slum communities. Interventions were also planned for women working in informal workplaces. We impacted over 1.42 million lives.
Empowering sanitation workers: With focused sanitation safety, short-term relief and skilling, and entrepreneurial livelihood programs, the IPA has built the long-term resilience of more than 0.082 million sanitation workers.
Key Learnings & Takeaways
1. Collaboration across 59 funders and 52 implementation and knowledge partners quickly proved the potential of a collective impact that can be envisioned for any prospective project.
2. These learnings further underlined the need of building medium to long term infrastructural and training solutions to strengthen the health systems of India.
3. The importance of agility within organisations to take swift strategic decisions and act on them, especially during a crisis, plays a crucial role in effective and timely relief management.
4. Partnerships with the Government are critical and could unlock significant scale-up opportunities.
IPA’s Response to India’s second wave of COVID-19
IPA Supporting Public Institutions
#PehnoSahi – A corporate mask wearing initiative
Additionally, the Alliance collectively championed mask usage through an online campaign called #Pehnosahi. The campaign was shared by several industry leaders and Alliance members to urge their employees and networks to wear masks correctly for a safe back-to-work transition.
TESTIMONIALS
“The team at the India Protectors Alliance has impressed us with their national reach – from Maharashtra, to Delhi, to Kolkata – to support our frontline healthcare and sanitation workers during the COVID-19 crisis. Thanks to their guidance, our support for critical hospital equipment and PPE kits across these critical locations was executed in a timely, hassle-free manner.”
– Sandeep Batra – Chief Financial Officer, Crompton Greaves
“India Protectors Alliance was extremely helpful and effective in gathering the COVID-19 needs from our stakeholder communities. Its widespread implementation network and total commitment enabled us to expeditiously support the healthcare workers within these communities through the distribution of PPE kits.”
– Sudhanshu Vats – Chief Executive Officer, Essel Propack