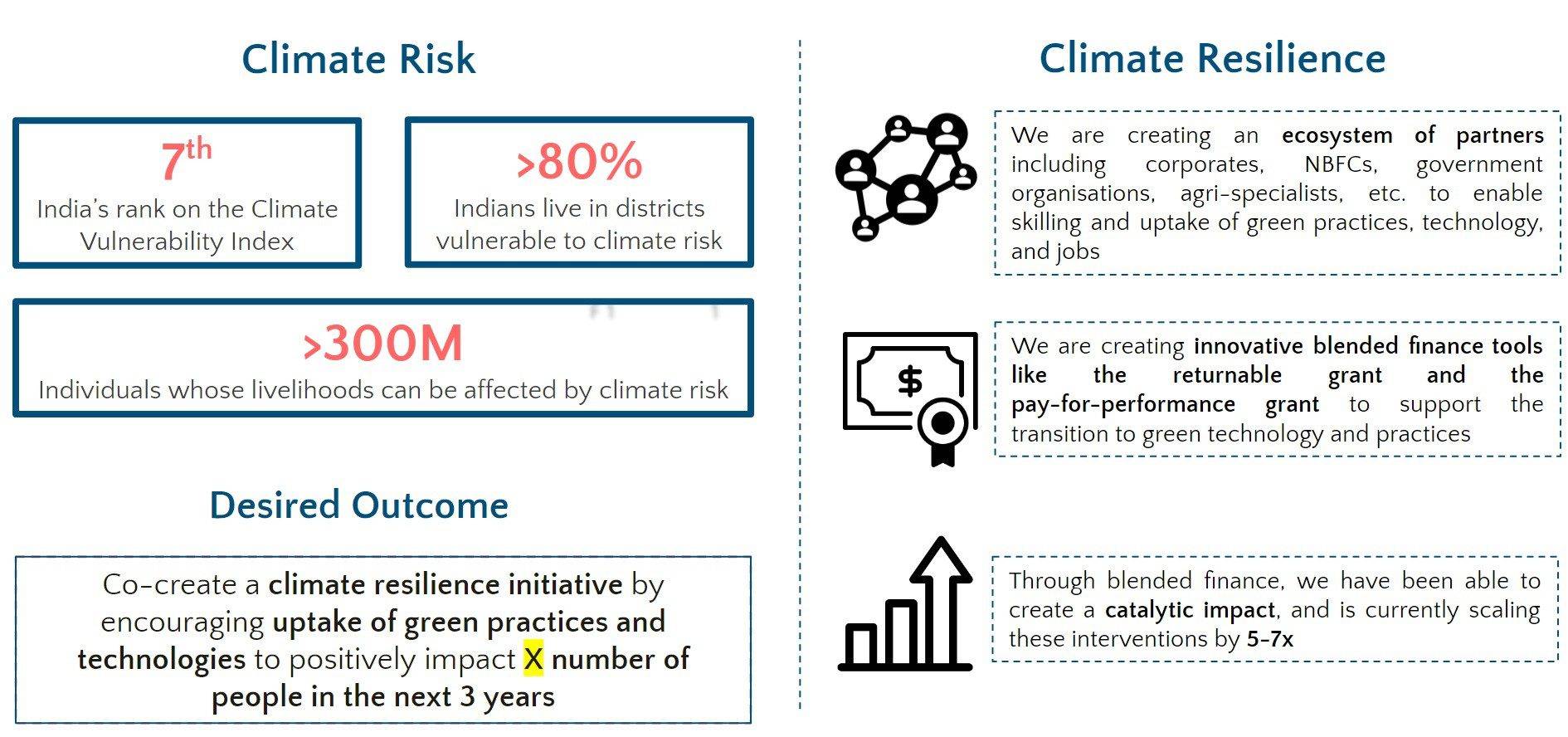
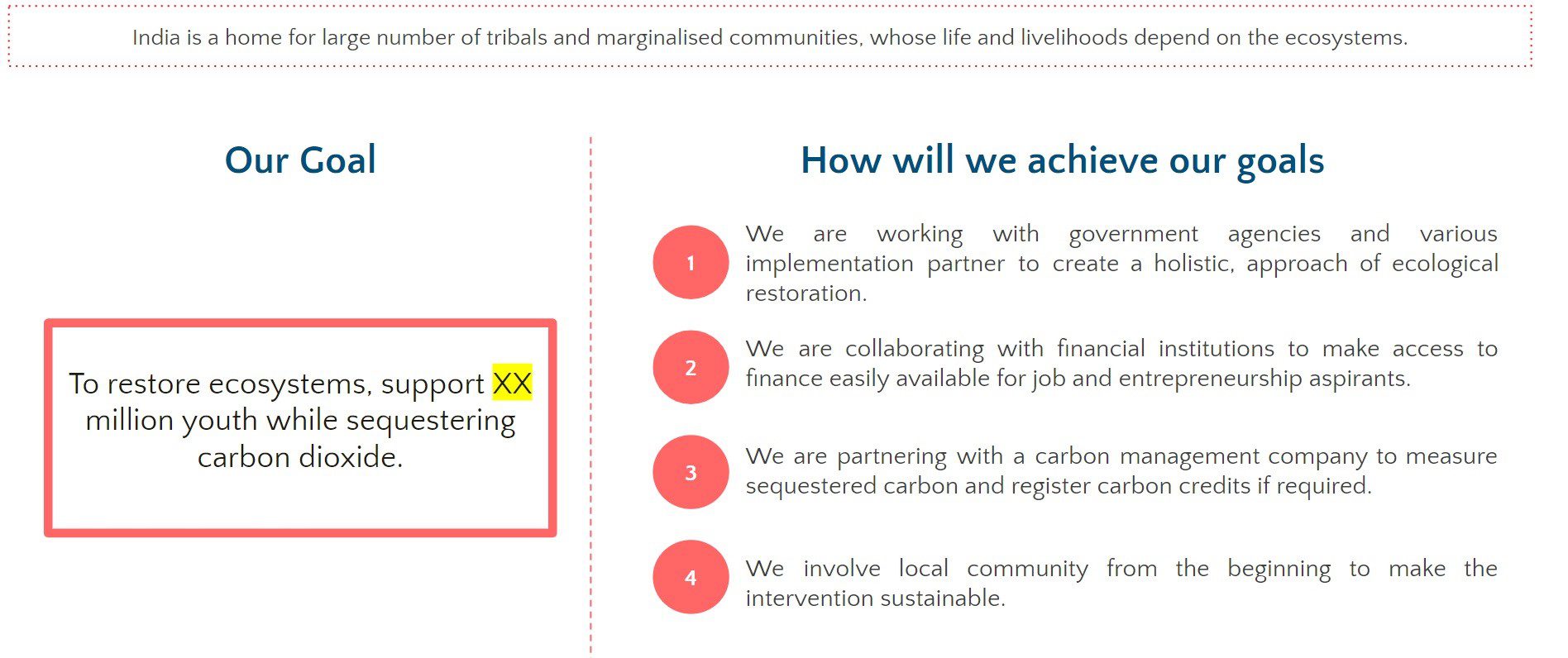
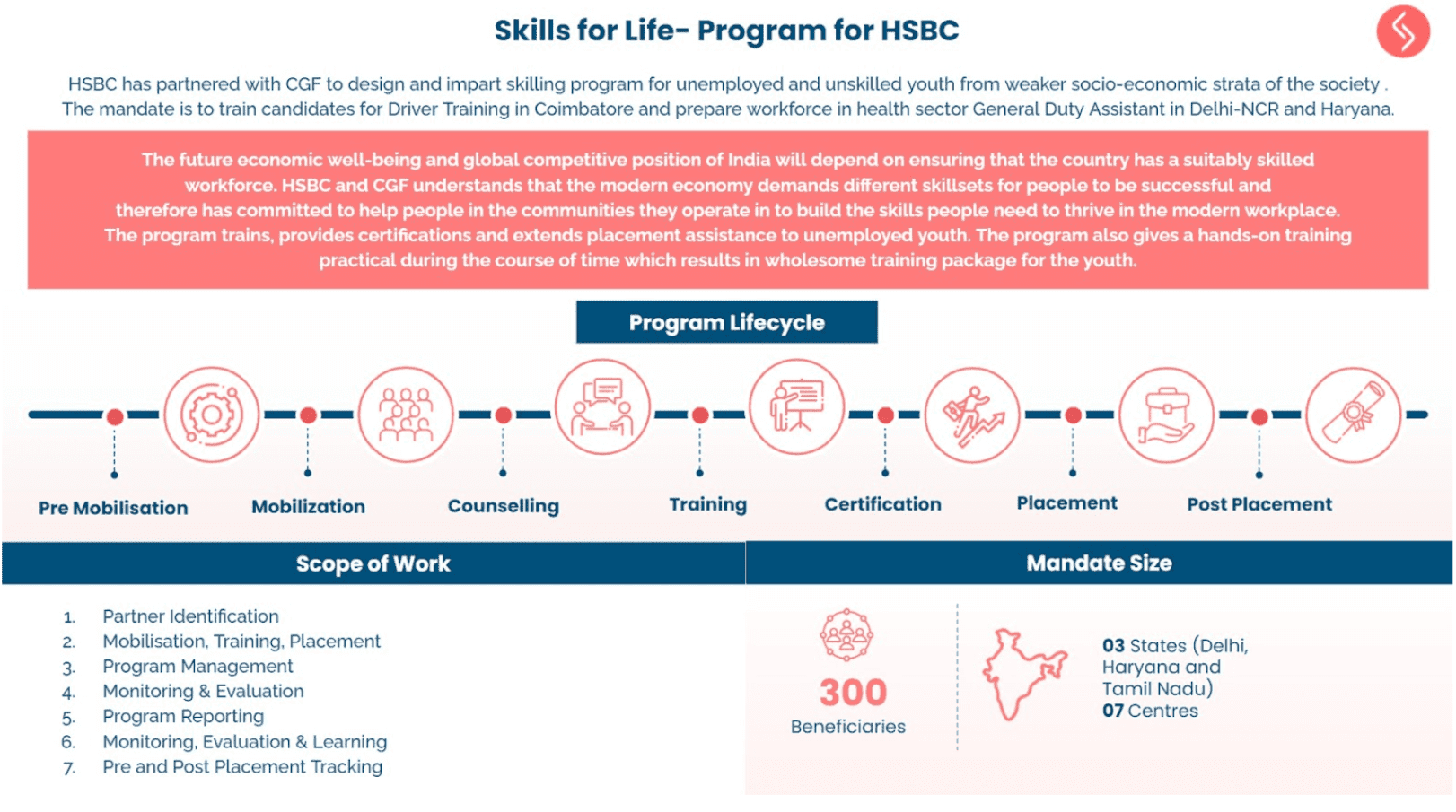
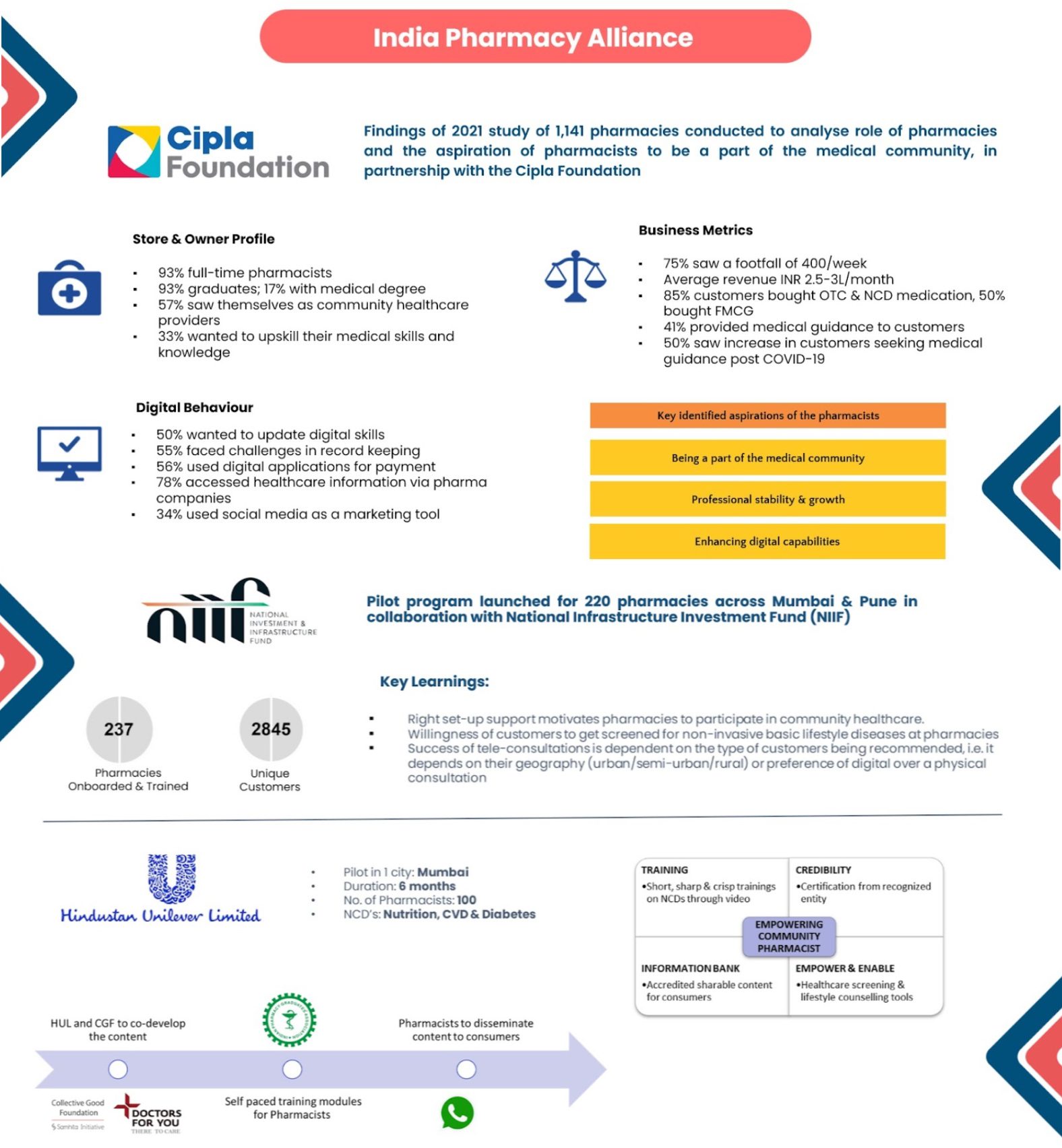
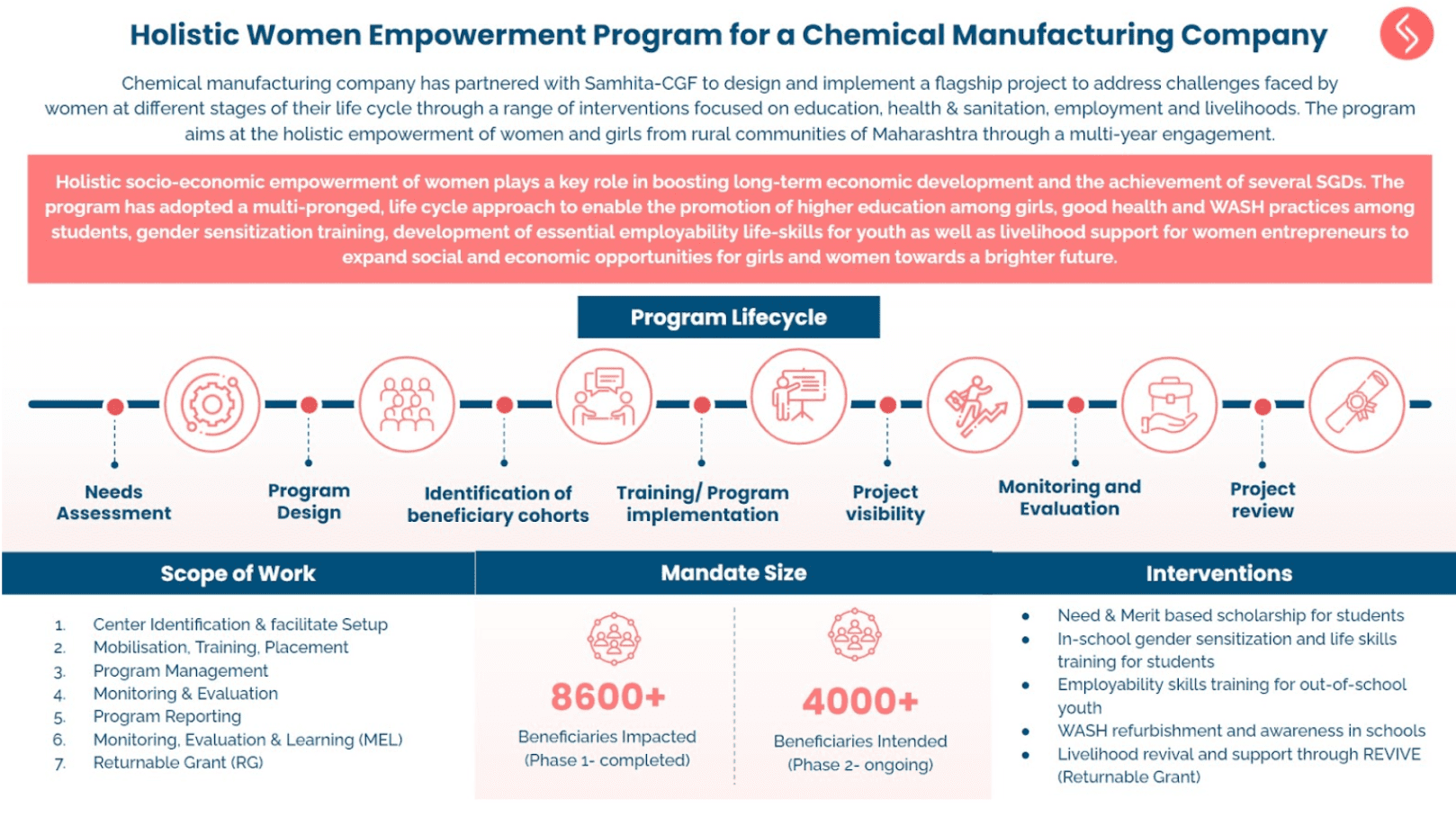
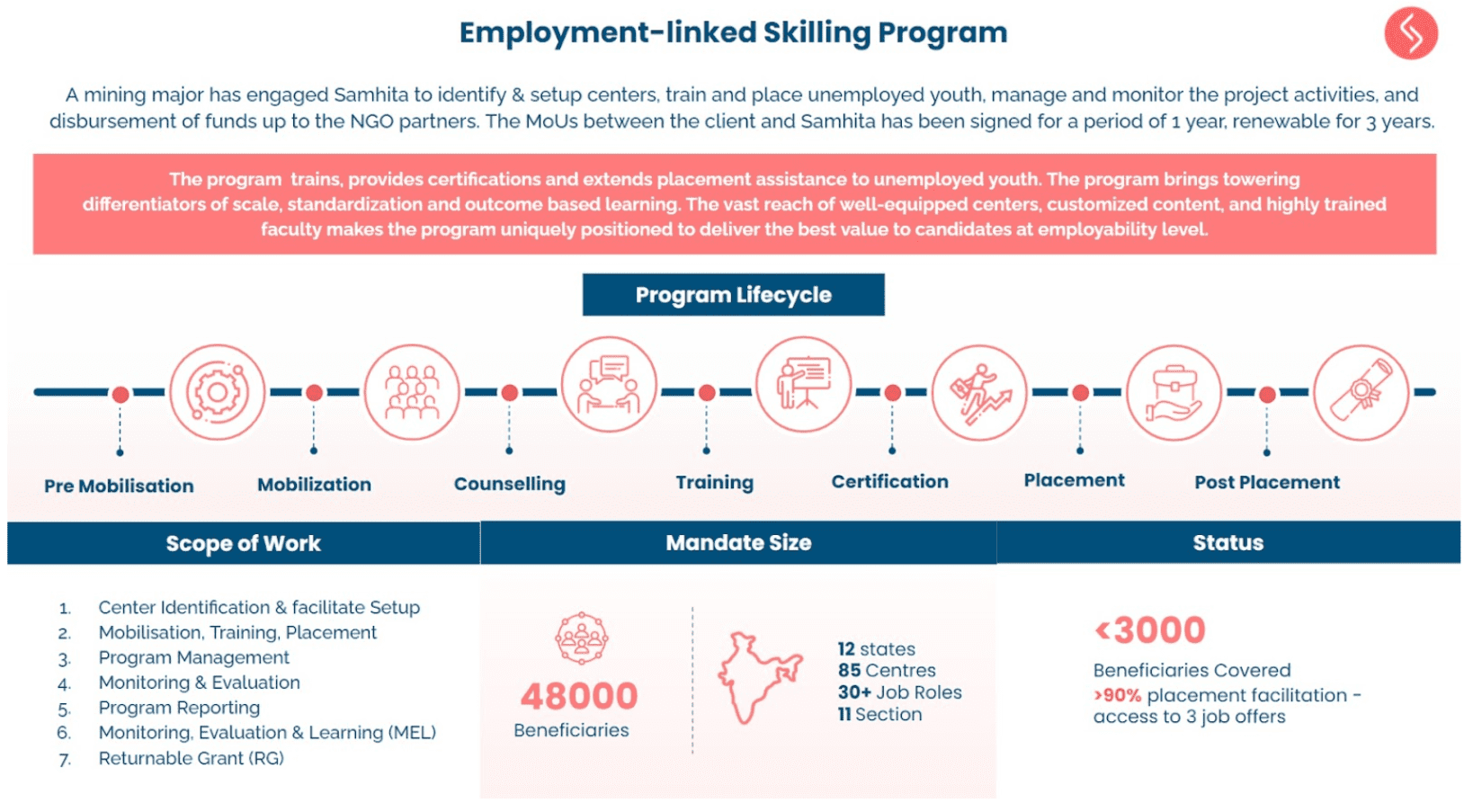
It’s been five years since India became the first country in the world to mandate Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) spending for eligible companies, generating a lot of local discussions, national debates and global curiosity.
Did the companies comply? How did they perform? How were the CSR funds spent and on what? Did the NGO sector benefit? What next for CSR?
We answer some of these questions here, based on the most comprehensive CSR dataset compiled so far by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs1 and our own experience with 100+ companies.
1. Compliance with CSR Act has been decent, with room for improvement
For a regulation that is only 5 years old, required companies to step outside their comfort zone and have a steep learning curve, the compliance has been good, with definite scope of improvement.
Compliance can be measured using two indicators – number of companies reporting on CSR and number of companies spending the stipulated amount.
- On average, the reporting rate among eligible companies in the last 4 years has been 64%.
- Companies spent 68% of the prescribed CSR amount in the last four years, totaling to ~INR 52,000 crore.
- Of the liable and reporting companies, the proportion spending zero amount has reduced over the years, consequentially, increasing the number of companies that actually do spend on CSR activities. In fact, the proportion spending exact or more than prescribed amount has increased from 26% in 14-15 to 44% in 17-18.

Data pertaining to CSR expenditure in FY 2017-18 is still being gathered by MCA through the filings made by companies and the numbers are likely to improve as more companies file their data.
2. The 80-20 rule
In 17-18, 289 companies spent INR 7,067 crore on CSR – even though these accounted for only 2% of liable and reporting companies, their cumulative spend amounted to 53% of the total spend on CSR in that year.
Many of these companies have adopted a strategic, systematic and structured approach to CSR, with the intent to maximize social impact. For instance, a majority of the BSE 100 companies, which are India’s largest companies by market cap, have created suitable internal governance structure to execute CSR, with 24% having their own foundation and 52% having dedicated CSR departments.
However, these companies also saw the highest gap between prescribed and spent CSR amounts, in absolute terms. If these companies can be further nudged and supported to spend their entire prescribed CSR amounts, and in more meaningful ways, we will not only be able to unlock a huge amount of capital for the development sector, but also significantly improve the quality of that capital.
3. Companies do not prefer writing cheques to government funds
CSR towards government funds such as Swachh Bharat Kosh, Clean Ganga Fund and Prime Minister’s Relief Fund collectively accounted for just 5% of the total CSR spend over 14-15 to 17-18. This signals to an underlying trend that companies are not merely looking to offload their CSR funds to simply comply with the Act, but are seeking opportunities to create deeper social impact by taking a more hands-on role.
4. CSR’s preference for education and health continues to leave out other causes
Education accounted for 30% of total CSR spending between 14-15 and 17-18. Healthcare was the second most popular cause, receiving 17% of funds, followed by rural development at 10%. On the other hand, women empowerment received 1%, training to promote sports received 1% and technology incubators received 0.13%.
5. Need vs. flow
CSR is benefitting states with relatively higher level of development. Maharashtra, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Tamil Nadu and Delhi received 40% of the total CSR expenditure from 2014-15 to 2017-18, even though they account for 11% of total number of aspirational districts. On the other hand, Jharkhand, Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Odisha, Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh account for 58% of total number of aspirational districts, yet received only 9% of the total expenditure towards CSR.
This bias continues within a state as well. An analysis of data for FY 16-17 shows that even in Maharashtra, which received the largest volume of funding, certain districts such as Pune and Mumbai (suburban) received the highest amount in CSR funding (more than INR 200 crore each), while those which were farther away from industrialized areas such as Hingoli, Buldhana and Parbhani received less than INR 1 crore of funding.

6. Local area spending becomes a double-edged sword
Subsection 5 of Section 135 encourages companies to give preference to the areas around where they operate, for spending the amount earmarked for CSR activities. CSR spending in local areas has accounted for a little more than half of the total CSR spend in the last two years.
This has had positive and negative ramifications. On the bright side, companies with manufacturing operations in remote parts of the country are investing in communities around them and working with smaller, local NGOs in doing so. But, by the same logic, significant CSR funds are being concentrating into small areas, leaving out surrounding areas with high needs but outside the subjective definitions of ‘local area’.

7. CSR’s promise for the NGO sector yet to be fully unlocked
While a substantial proportion of companies spend their CSR funds directly, implying through vendors or service providers that are not not-for-profit in nature, NGOs are becoming the most popular route for companies to execute their CSR activities. 43% of all CSR funds in the last four years was spent through supporting NGOs with grants.
However, not all NGOs have been able to tap into this opportunity. An NGO survey2 conducted by Samhita, in association with the ATE Foundation, in 2019 revealed that 1 out of 2 NGOs had not received CSR funds in the last one year. Lack of information on corporate opportunities, absence of an understanding to deal with CSR requirements and NGO’s location were the top three challenges reported by NGOs in accessing CSR.

What next for CSR?
A. From compliance to strategic to catalytic
Many companies have graduated from compliance-oriented CSR to strategic CSR, to now thinking of being catalytic.
Catalytic CSR is defined by its ability to:
- Unlock more resources and generate leverage by seeding the flow of risk capital (philanthropic or commercial)
- Address market failures or inefficiencies in an ecosystem
- Reduce transaction costs and information asymmetry between various actors
- Introduce new stakeholders to the ecosystem and leverage their competencies
B. Emphasis on flagship programs
The desire to be strategic has encouraged companies to play a proactive and hands-on role in their CSR programs. More and more companies want to co-create ‘flagship’ programs that leverage their business strengths in meaningfully addressing a social issue and differentiate them in the sector. Flagship CSR programs are great since they bring more corporate ownership, significant resources, innovative thinking, long-term commitment and a comprehensive approach. However, they may also lead to higher expectations around performance, systems and processes from the NGO partners executing such programs.
C. Data-driven decisions and evidence-backed interventions
CSR has emphasized strong M&E systems from the get-go. Many companies base their decisions to fund, scale or exit based on data and evidence generated through process and outcome evaluations. In a further impetus, the High Level Committee on CSR, constituted by the MCA, has suggested that companies with CSR budgets of INR 5 crore or more invest in impact evaluations at least once on three years. Further, with the recognition of Nobel Laureate Abhijit Banerjee, Esther Duflo and Micheal Kremer’s work regarding experimental approach to alleviating global poverty3 wherein rigorous evidence is used to inform policy, CSR may move towards not only funding and scaling evidence-backed interventions, but also improving the quality of their own impact assessments.
D. Rising interest in innovative financial instruments
India has witnessed a lot of traction in the use of innovative financial instruments in the social and development sector. A prominent example of this was the launch of the world’s first development impact bond in India which focused on the learning and enrollment outcomes for out-of-school girls.4 These trends coupled with the proposed institutionalization of a social stock exchange in India, as declared by Nirmala Sitharaman in her maiden budget speech5, has the potential to drive companies to invest in innovative financial instruments such as development impact bonds, social success notes, loan guarantee funds etc.
E. Brands with purpose – moving beyond CSR
Companies have started moving from CSR to a broader narrative of responsible corporate citizenship, of which CSR is just one part that talks about responsibility to external communities and environment. The other part of the narrative is sustainable and responsible internal business practices in supply chains, production, distribution etc. This trend is being driven by two factors –
- A growing interest and awareness of ESG (environmental, social and corporate governance) factors among investors in India
- A growing conscious consumer movement that is building pressure on companies to respond to ethical and environmental issues that matter to them
Samhita Social Ventures stands out far and away as the best organization we have worked with. The Samhita team were absolutely fabulous throughout – from initial planning, to site preparation, participant interaction, event execution, post-event interaction and reporting. The USIP would highly recommend them without reservation to anyone looking to initiate high impact projects.– PeaceTechLab
United States Institute of Peace
The team at Samhita has been instrumental in building an executable module for Support A Woman. Their expertise in working with NGOs and understanding corporate priorities at the same time has helped immensely in smooth execution of the program– Johnson & Johnson
Samhita has been our trusted partner in the EdelGive Social Innovation Honours for two years. Adept management of the end-to-end online application process and widespread outreach resulted in large increases in the number of quality applications from NGOs across India. Samhita’s strength lies in their extensive NGO network and a very professional and committed team– EdelGive Foundation