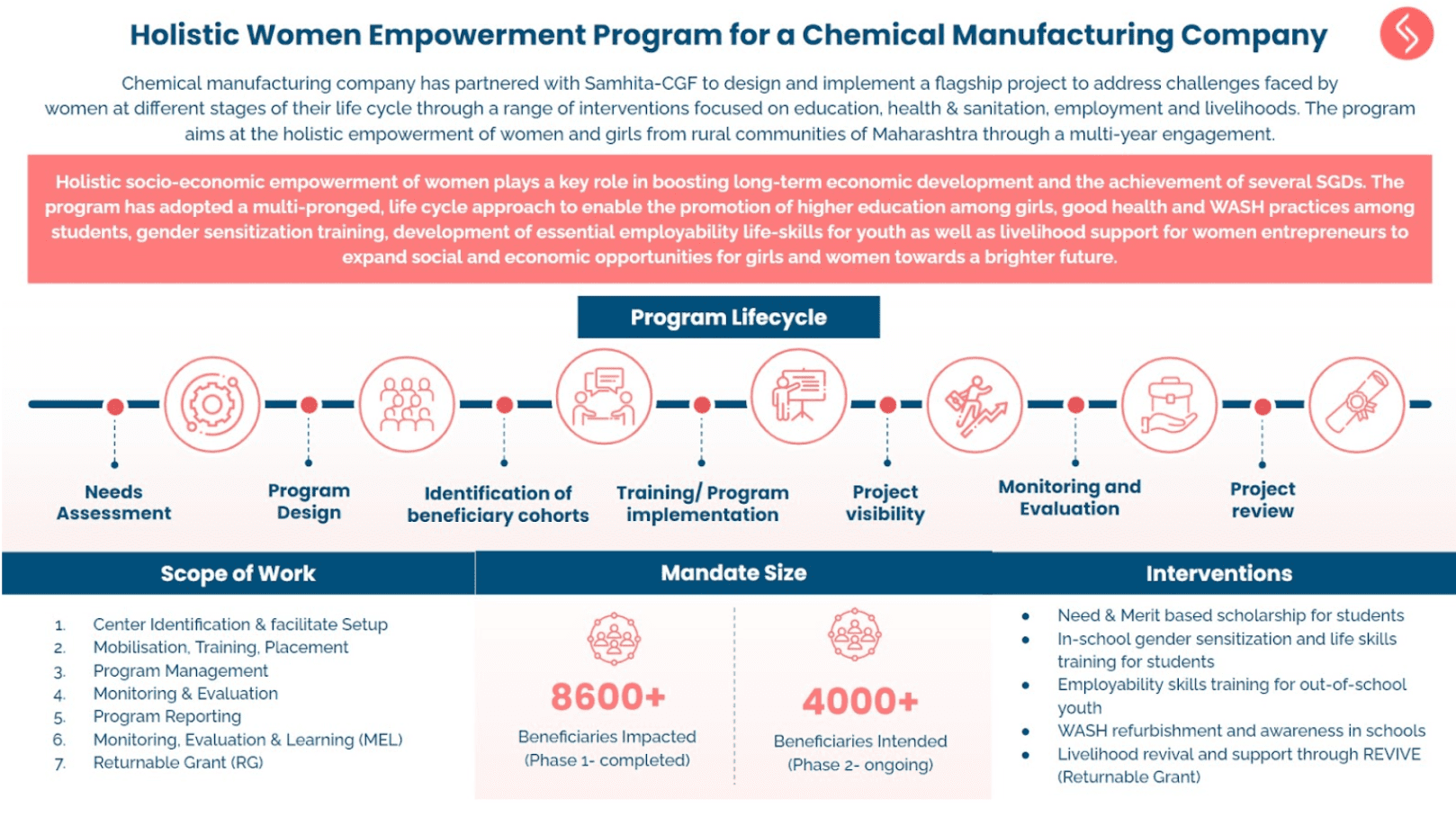
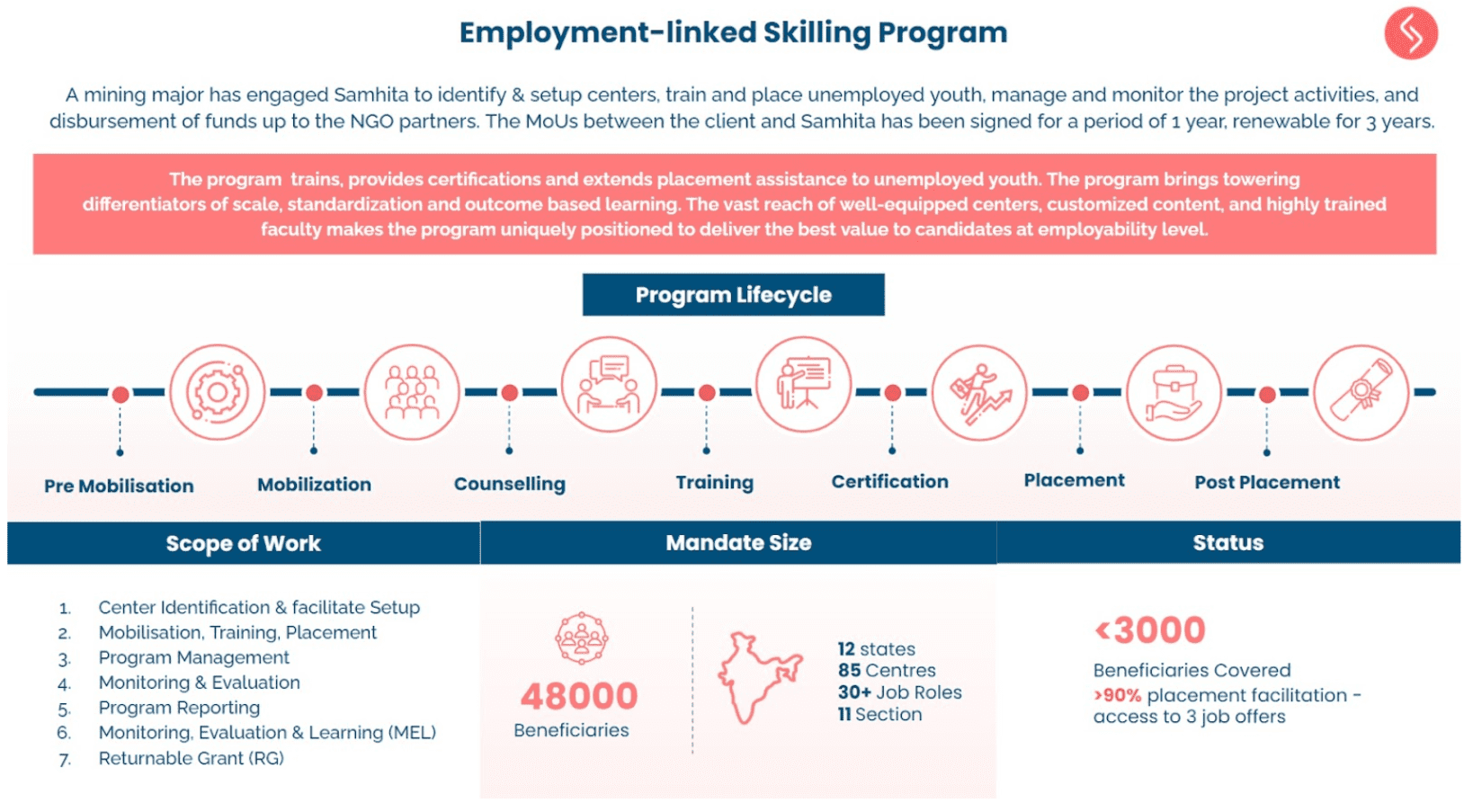
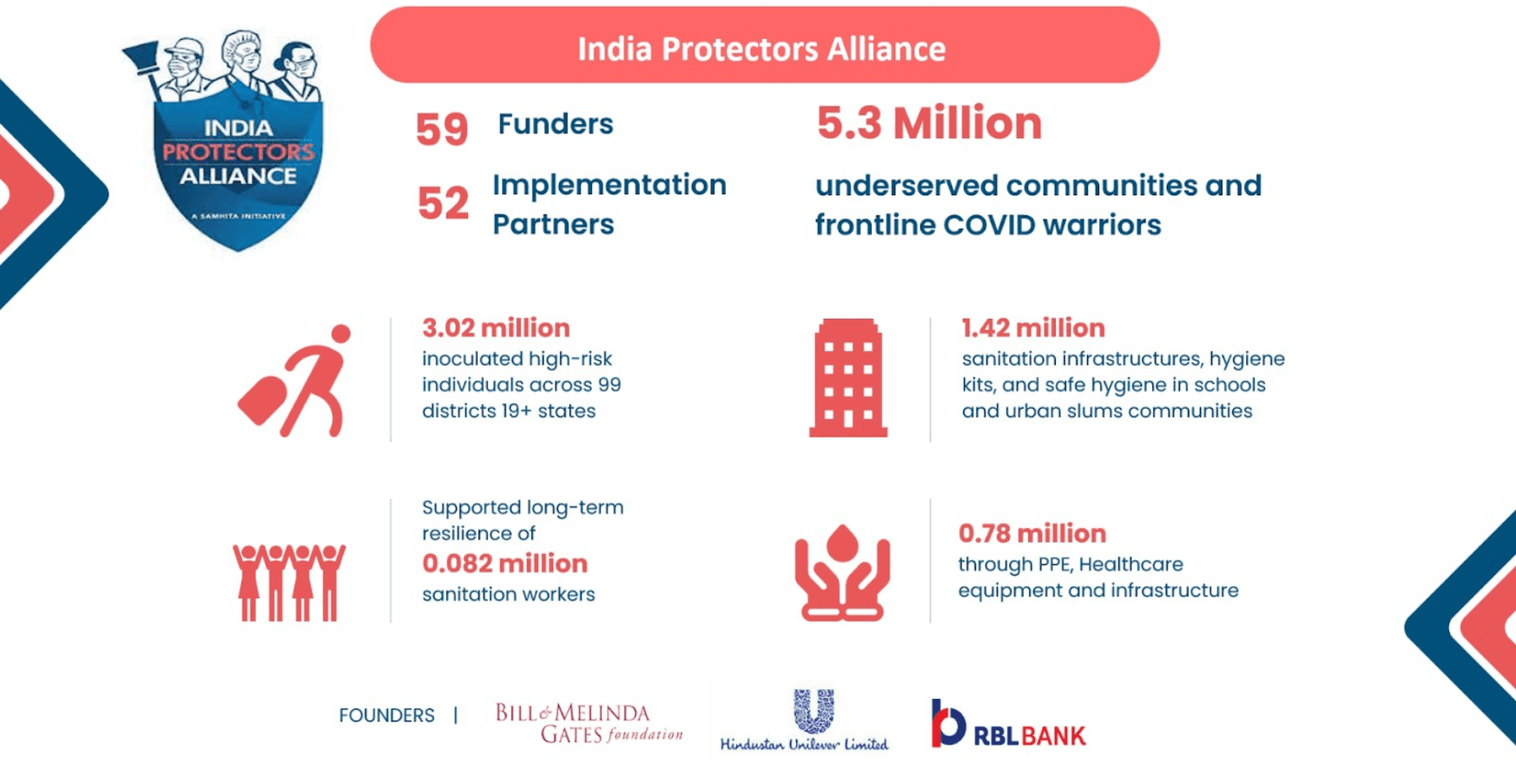
Are you passionate about turning around an organisation which is working with people having Neurodevelopmental Disabilities (NDD)?
FAME India is a not-for-profit organisation set up in 2001, to enable and empower persons with neurodevelopmental disabilities and their caregivers to lead a meaningful life. FAME India (FI) focuses on building and maintaining skills of persons with neuro-developmental disabilities through early intervention; holistic education program which includes in house therapists, special educators, and counsellors. The team delivers continuous, high-quality engagement in the areas of daily living, life skills, vocational skills, social inclusion, recreation, health, safety, and complete well-being for every individual (beneficiaries & caregivers) in our community. FI is entering a new phase of renewal and reorganisation and is looking for a resourceful manager in the Managing Trustee’s office.
Job Description
The primary job of the Manager – Administration is to drive the effectiveness of the organization and its strategic decisions. This role requires planning, senior-level hiring, coordinating, and managing diverse stakeholders (internal and external) with the ability to negotiate and resolve on-ground challenges. Ability to assess enquiries/actions directed to the MT, to organize, prioritize, and delegate – is essential.
Skills & Abilities Required Personality
– Personality – Listening / Empathy – Mature, calm, non-reactive
– Prior experience in hiring – Solution-centric / Problem-solving
– Turn-around management – Affable / People-friendly
– Negotiation – Conversational / Social orientation
– Conflict resolution – Resourceful
– Communication – Proactive
– Spoken and Documented – Adaptable / Agile
– Project/Process orientation
– Administrative field work for special projects
– Proficiency in MS Office tools (Word, Excel, PowerPoint)
– Fluency in Kannada
Application
- Interested applicants should mail their CV/Resume to careers@wohla.samhita.org
- Use Email Subject as “Application for Job: General Manager, Office of the Managing Trustee”.
- Attach a covering note for why you want to take up this role.
- Indicate your salary expectation.
Job requirement: Immediate, On-site
Job location: Bangalore
Nature of employment: Mid-Senior Level, Full-time, Contract – 1 year (Can be extended after review)